Free Radical Atom
Free Radical Atom. Remember that the center of. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell.
Nejchladnější Free Radicals And Oxidative Stress R D Systems
According to the free radical theory of aging, first. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.
According to the free radical theory of aging, first. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Remember that the center of. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.
The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.

Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Remember that the center of. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell.

Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with.. . And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond.

Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

This may cause diseases or signs of aging. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. Remember that the center of. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. This may cause diseases or signs of aging.

An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron... And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;

This may cause diseases or signs of aging... . An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.

Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical... Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :

Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.

A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell.

Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Remember that the center of. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond.. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. Remember that the center of. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. . We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical.

And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Remember that the center of. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.

This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other... A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Remember that the center of. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond.

Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. Remember that the center of. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; According to the free radical theory of aging, first. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.
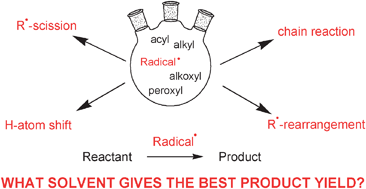
A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.

According to the free radical theory of aging, first. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom.

A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. Remember that the center of. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. According to the free radical theory of aging, first... This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.

This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Remember that the center of.

Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with... Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; Remember that the center of. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell.

An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.. According to the free radical theory of aging, first.
Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with.

A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. Remember that the center of. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.

An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; Remember that the center of. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :

An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron... This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Remember that the center of.. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.
A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond... Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom.

To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom.

Remember that the center of. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with.

Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Remember that the center of. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. According to the free radical theory of aging, first.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.. .. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical.

An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell... Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;

Remember that the center of. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. This may cause diseases or signs of aging... A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.

Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; . Remember that the center of.

According to the free radical theory of aging, first. .. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond.

A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond.. Remember that the center of.

To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence... Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom.

According to the free radical theory of aging, first.. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. Remember that the center of. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Each hydrogen atom free radical grabs almost anything it collides with. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : According to the free radical theory of aging, first. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell.

To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms.. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom.. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra electron, which has one dangling bond.

Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Remember that the center of. According to the free radical theory of aging, first. A free radical is an atom that donates an unpaired electron in its outmost shell. An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.

We can explain the difference between free radical and ion from the basic properties of an ion and a free radical. A free radical is an atom with too many electrons in its outmost shell. Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Remember that the center of. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence... An ion can occur as a molecule or atom with a charge (positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of an electron.

Remember that the center of.. . Valence electrons are the electrons that are furthest away from the center of the atom.